Exploring the Pros and Cons of Human Augmentation
8 min read Delve into the benefits and challenges of human augmentation and its impact on our future society and identity. (0 Reviews)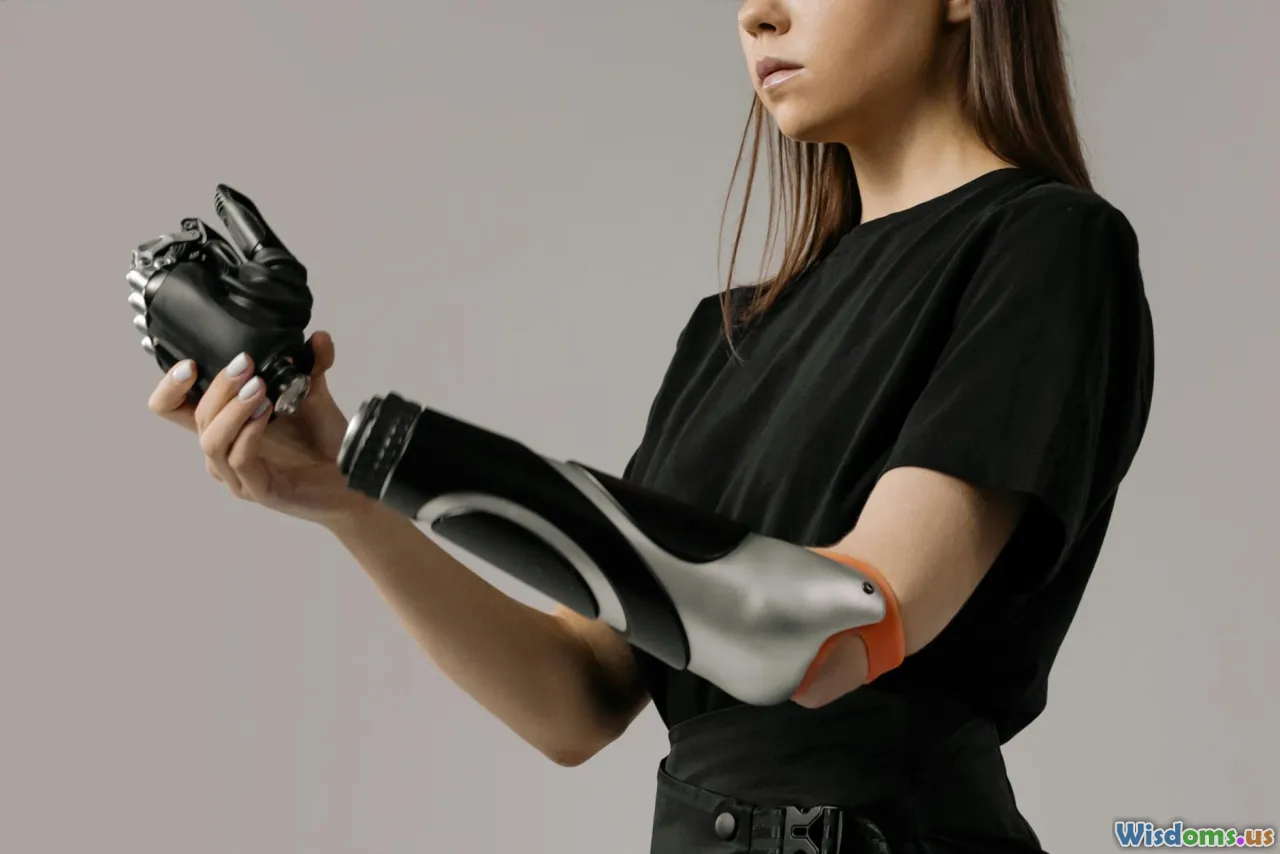
Exploring the Pros and Cons of Human Augmentation
Human augmentation, once the realm of science fiction, is rapidly becoming a tangible part of our near future. From embedded microchips enhancing memory recall to robotic exoskeletons boosting physical strength, the boundary between man and machine continues to blur. But as this technology advances, it raises an array of critical questions: What advantages will it bring, and what risks must we prepare to face? This article explores the multifaceted pros and cons of human augmentation, providing insight into a technological revolution poised to redefine humanity itself.
What is Human Augmentation?
Human augmentation refers to the use of technology to enhance human abilities, either physically, cognitively, or sensorily. These enhancements can range from prosthetic limbs restoring mobility to advanced neural implants improving cognitive function.
Currently, human augmentation technologies fall into several categories:
- Physical augmentation: Exoskeletons and prosthetics that enhance strength or restore mobility.
- Cognitive augmentation: Brain-machine interfaces and neural implants aimed at boosting memory, processing speed, or sensory perception.
- Sensory augmentation: Devices that enhance existing senses or introduce new ones, such as infrared vision or ultrasonic hearing.
The inspiration behind many of these developments can be traced back to speculative fiction classics like Ghost in the Shell or Blade Runner, where human-machine fusion explores complex social and ethical landscapes.
The Advantages of Human Augmentation
1. Medical and Health Benefits
Arguably the most immediate benefit of human augmentation lies in healthcare. For individuals with disabilities, prosthetics and neural implants offer life-changing possibilities. Cochlear implants have already restored hearing to over 320,000 users worldwide as of recent data, transforming communication for those with deafness.
Additionally, augmentations that enhance neuroplasticity could one day help rehabilitate stroke victims or patients with neurodegenerative diseases. Exoskeletons are enabling paraplegics to walk again; the Ekso Bionics suit, for example, helps users regain mobility, improving quality of life tremendously.
2. Enhanced Human Performance
Beyond restorative applications, augmentation holds promising prospects for improving human performance. Military and industrial sectors invest heavily in exoskeletons that reduce worker fatigue and prevent injury. The U.S. Army’s Tactical Augmentation Combat Suit demonstrates how such technologies can give soldiers enhanced endurance and strength.
Cognitive augmentation could accelerate learning and problem-solving abilities. Neural implants like Elon Musk’s Neuralink aim to directly interface with the brain, potentially enabling faster communication and data processing.
3. New Frontiers in Creativity and Interaction
Human augmentation may redefine human creativity. Enhanced sensory input devices and brain-computer interfaces could open novel ways to create, from music influenced by new senses to immersive virtual environments experienced directly through neural links.
Moreover, augmented cognition might facilitate empathy by enabling shared emotional experiences or complex data visualization directly in the mind.
The Challenges and Risks of Human Augmentation
1. Ethical and Social Implications
With great power comes complex ethical dilemmas. Who will have access to augmentation technologies? If enhancements are costly, a deep societal divide may emerge between “augmented” and “non-augmented” individuals, exacerbating inequality.
The prospect of altering fundamental aspects of human identity raises profound questions. Philosopher Nick Bostrom warns of "the posthuman dilemma," where human nature itself is questioned. If cognitive or emotional capacities are extensively modified, what does it mean to remain human?
2. Privacy and Security Concerns
Brain-computer interfaces connected to the internet risk exposing users to unprecedented hacking threats. In 2021, security researchers demonstrated vulnerabilities in implantable medical devices — a hint at potential future risks if augmented humans become targets for cyber attacks.
Data collected from these augmentations could be misused by governments or corporations for control or surveillance, compromising autonomy and privacy.
3. Psychological and Physiological Risks
The long-term physiological impacts of neural implants remain largely unknown. Could extensive interface with machines cause unforeseen cognitive or neurological side effects? Cases of "device rejection" in prosthetics show that incompatibility or infection risks persist.
Psychologically, adapting to enhanced abilities might cause identity disruptions or social isolation.
Real-World Examples of Human Augmentation Today
-
Bionic limbs: Oscar Pistorius, a double amputee sprinter, used carbon-fiber prosthetic legs to compete on the world stage, raising debates about fairness and augmentation in sports.
-
Neural Implants: The FDA-approved BrainGate system allows paralyzed users to control computers with their thoughts, signaling the dawn of direct brain-machine communication.
-
Exoskeletons for Industry: Companies like Hyundai and Ford use wearable suits to reduce worker fatigue and injury risks.
These examples illustrate both the transformative potential of augmentation and the complexity of associated issues.
Conclusion: Balancing Innovation with Responsibility
Human augmentation stands on the frontier of science fiction and reality, offering unprecedented opportunities to extend and enhance human capabilities. From restoring lost functions to pushing the boundaries of cognition and performance, the promise is tremendous.
However, alongside these benefits come significant ethical, social, and health considerations. Policymakers, technologists, and society at large must navigate this evolving landscape thoughtfully to ensure augmentation technologies serve humanity’s best interests without compromising equity, identity, or safety.
The promise of human augmentation may ultimately depend not just on technological breakthroughs but on our collective decisions regarding its development and deployment. By actively engaging in these discussions today, we can shape a future where human and machine harmoniously enhance our potential without sacrificing core values.
References:
- Bostrom, Nick. "The Posthuman Dilemma." Philosophy & Technology, 2005.
- Ekso Bionics Exoskeleton Overview. https://eksobionics.com
- FDA-approved BrainGate System Clinical Trials. Neuroengineering Journal, 2022.
- Security Risks of Medical Devices. Avancha et al., Health IT Security, 2021.
- Oscar Pistorius and the Ethics of Augmentation in Sports. Journal of Sports Ethics, 2014.
Rate the Post
User Reviews
Popular Posts