The Future of Dream Therapy BrainTech Predictions for Wellness
7 min read Explore groundbreaking BrainTech advancements reshaping dream therapy and wellness with scientific insights and futuristic predictions. (0 Reviews)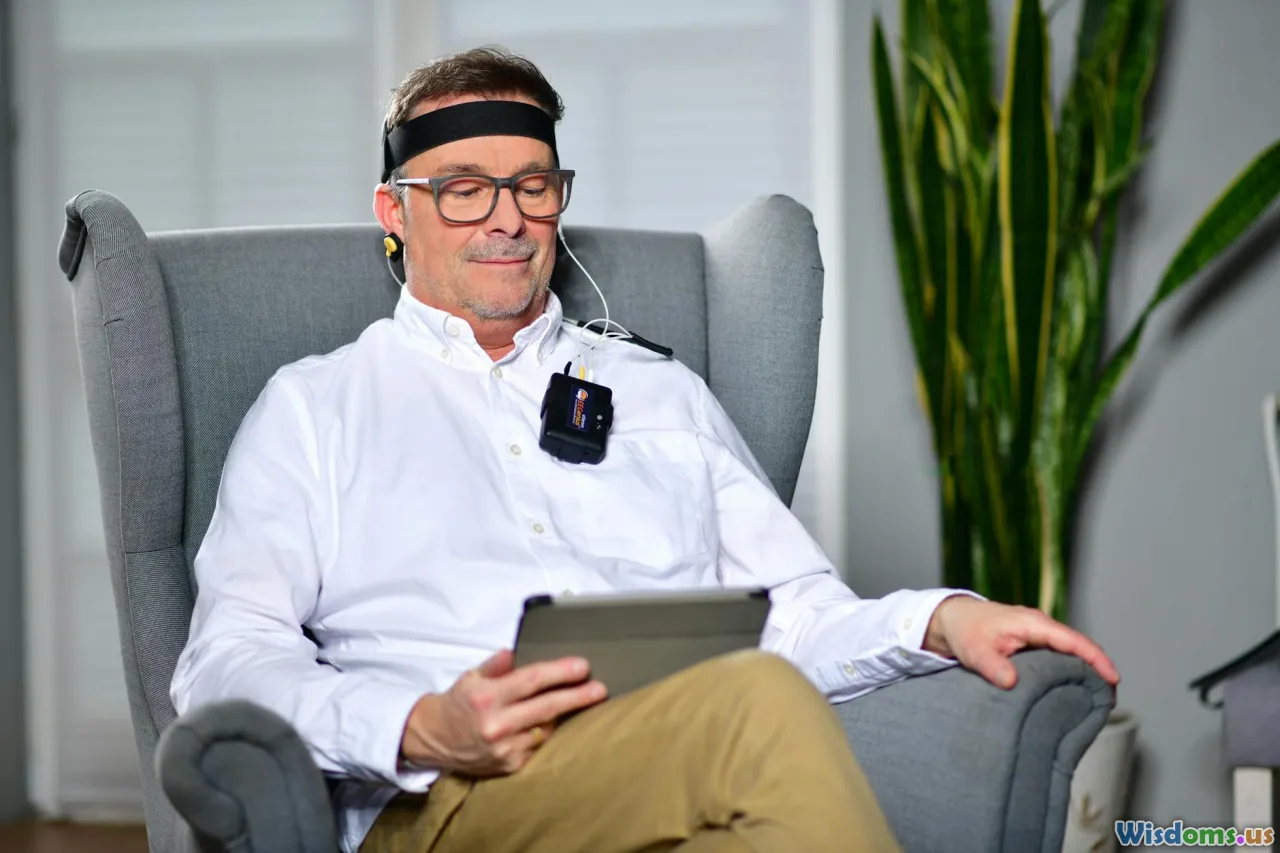
The Future of Dream Therapy: BrainTech Predictions for Wellness
Dreams have fascinated humanity for millennia, acting as both mysterious self-reflections and windows to our subconscious minds. Yet, it is only recently—with incredible advancements in brain science and technology—that we are beginning to truly understand and even harness dreams to promote wellness. In this article, we’ll explore the cutting-edge BrainTech shaping the future of dream therapy and reveal how these innovations offer promising pathways for enhancing mental and emotional health.
Introduction: Why Dream Therapy Matters Now More Than Ever
With rising global mental health challenges such as anxiety, depression, and PTSD, new therapeutic arenas are being explored urgently. Dream therapy, traditionally involving interpretation and psychoanalytic approaches, is evolving thanks to brain science and technology. Dreams reveal cognitive and emotional processing occurring in sleep, making them crucial windows into mental wellness.
Imagine a future where tailored neurodevices monitor and influence your dreams to reduce trauma symptoms or optimize creativity. This is not science fiction but an emerging reality enabled by advances in neural imaging, AI, and neuromodulation.
Unlocking the Brain's Nocturnal Activity: Scientific Foundations
Dreams primarily occur during rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. Neuroscientists use functional MRI (fMRI), EEG, and new methods such as near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) to map brain activity during dreaming phases.
For instance, a landmark 2017 study by Yukiyasu Kamitani’s group in Japan decoded rudimentary visual images from dreams by analyzing brain signals—a clear demonstration that dreams can be quantified and even interpreted using technology. This mapping provides the foundation for interventions that could one day steer or reconstruct dream content for therapeutic benefit.
BrainTech Innovations Shaping Dream Therapy
1. Neurofeedback and Dream Monitoring Devices
Wearable EEG headbands and smart pillows equipped with biosensors are already capturing sleep data. Leading companies like Dreem and Muse offer devices that not only track REM phases but also provide neurofeedback to help users achieve better dream quality and sleep patterns.
Coupled with AI algorithms, these devices are progressing towards providing real-time dream analysis, helping individuals identify nightmares and recurrent patterns linked with mental health issues.
2. Targeted Memory Reactivation (TMR)
TMR is a technique where specific sounds or cues are played during sleep to prompt the reactivation of memories or emotions linked with those cues. Initial trials have demonstrated that TMR can enhance learning and mitigate nightmares by subtly steering dream themes.
A 2020 study published in Science Advances found that mild auditory stimulation helped patients with PTSD reduce distressing dreams by interfering with the consolidation of negative memory during REM.
3. Transcranial Electrical Stimulation (tES) and Dream Modulation
tES methods like transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) or alternating current stimulation (tACS) are used to modulate brain activity non-invasively. Researchers are exploring how these can influence the regions of the brain active during dreaming to improve emotional processing or creativity.
For example, stimulating the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex during REM sleep improved dream lucidity—a state where the dreamer becomes aware and may control their dream—which has implications for therapeutic dream control.
Real-World Applications and Wellness Impact
PTSD and Trauma Recovery
Nightmares are a hallmark of PTSD. Utilizing BrainTech to monitor sleep, trigger positive dream cues, or suppress anxiety-inducing neuronal pathways is an emerging therapeutic avenue. The VA hospital system and partners are investing in trials that incorporate dream feedback alongside cognitive behavioral therapy.
Enhancing Creativity and Problem-Solving
Dreams foster novel connections that wake cognition cannot easily produce. Tech-enhanced dream lucidity could help artists, scientists, and innovators tap into subconscious problem-solving, potentially revolutionizing creative industries.
Personalized Mental Health Interventions
Future BrainTech will integrate dream data with biometric and mood-tracking inputs, enabling personalized wellness plans. For example, if a user experiences persistent negative dream themes, their therapy might be adjusted dynamically with targeted neurostimulation or guided dream incubation strategies.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges
While the promise is tremendous, manipulating dreams raises ethical questions: What constitutes informed consent when the brain is so vulnerable during sleep? How do we protect privacy when devices record intimate subconscious data? Regulation and ethical frameworks must evolve alongside technology.
Moreover, technical challenges remain in accurately decoding and influencing dreams without disrupting sleep quality or causing unintended psychological effects.
Predictions for the Next Decade
-
Integrated Dream Therapy Platforms: Combining AI-driven dream interpretation with neurostimulation and biosensors integrated into accessible consumer devices.
-
Neuropharmacological Adjuncts: Drugs designed to augment dream therapy by enhancing neuroplasticity during sleep.
-
Virtual Dream Environments: Using virtual and augmented reality to simulate dream-like experiences embedded with therapeutic goals.
-
Remote Dream Health Monitoring: Telehealth applications for clinicians to monitor and guide patients’ dream therapy sessions in real time.
Conclusion: Embracing a New Frontier in Wellness
The convergence of brain science and technology is poised to revolutionize our understanding and use of dreams in promoting mental health and wellness. As we learn to decode, guide, and even create therapeutic dreams, a new paradigm emerges: dream therapy enhanced by BrainTech can address complex emotional and cognitive challenges with unprecedented precision.
Staying informed and engaged with these innovations brings us closer to a future where our brain’s nocturnal narratives become powerful allies in wellbeing. Dream therapy’s future is vibrant, promising, and just beginning to unfold.
Rate the Post
User Reviews
Popular Posts