The Impact of Robotics in Medicine
7 min read Explore how robotics is transforming medicine, enhancing surgical precision, patient care, and the future of healthcare. (0 Reviews)
The Impact of Robotics in Medicine
Robotics has emerged as a transformative force in various sectors, and medicine is no exception. With advancements in technology, the integration of robotics in healthcare has not only improved surgical outcomes but also enhanced patient care and operational efficiency. In this article, we will explore the multifaceted impact of robotics in medicine, examining its applications, benefits, challenges, and future prospects.
1. Understanding Robotics in Medicine
Robotics in medicine involves the use of robotic systems to assist in surgical procedures, diagnostics, rehabilitation, and patient care. These robotic systems are designed to enhance the capabilities of healthcare professionals, allowing for greater precision and control during medical interventions.
1.1 Surgical Robotics
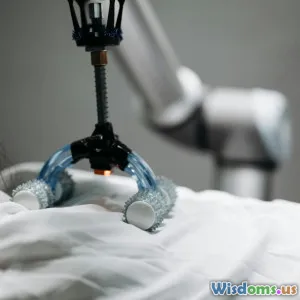
Surgical robotics, particularly minimally invasive surgery, has gained significant traction in recent years. Systems such as the da Vinci Surgical System have enabled surgeons to perform complex procedures through small incisions, resulting in reduced recovery times, less pain, and minimal scarring for patients. These robotic systems provide enhanced visualization, dexterity, and stability during surgery.
1.2 Rehabilitation Robotics
In the realm of rehabilitation, robotic devices have been developed to assist patients recovering from injuries or surgeries. Robotic exoskeletons and rehabilitation robots help patients regain mobility and strength through guided exercises. For example, devices like the Lokomat can assist individuals with spinal cord injuries to relearn walking patterns.
1.3 Robotic-Assisted Diagnostics
Robotics also plays a crucial role in diagnostics. Robotic systems can automate laboratory processes, manage samples, and analyze data, leading to faster and more accurate test results. This is particularly beneficial in fields like pathology, where robotic systems can assist in the analysis of tissue samples.
2. Benefits of Robotics in Medicine
The integration of robotics into healthcare offers numerous benefits:
2.1 Enhanced Precision and Control
Robotic systems provide surgeons with enhanced precision, allowing for intricate procedures to be performed with greater control. This minimizes the risk of complications and improves patient outcomes.
2.2 Reduced Recovery Times
Minimally invasive robotic surgeries typically result in shorter recovery times compared to traditional open surgeries. Patients experience less postoperative pain and can return to their daily activities more quickly.
2.3 Increased Efficiency
Robotic systems can streamline various healthcare processes, from surgery to diagnostics. Automation reduces the workload on healthcare professionals, allowing them to focus on patient care and improving overall efficiency in healthcare settings.
2.4 Improved Patient Safety
Robotics can enhance patient safety by reducing the likelihood of human error during surgical procedures. With advanced imaging and real-time data integration, robotic systems can provide crucial information to surgeons, ensuring better decision-making.
3. Challenges and Considerations
While the impact of robotics in medicine is largely positive, there are challenges and considerations that must be addressed:
3.1 High Costs
The initial investment in robotic systems can be substantial, creating barriers for some healthcare facilities. Ongoing maintenance and training costs also contribute to the overall expenses associated with robotic-assisted procedures.
3.2 Training and Adaptation
Healthcare professionals require specialized training to effectively use robotic systems. Ongoing education and adaptation to new technologies can be challenging, especially for those accustomed to traditional surgical methods.
3.3 Ethical Considerations
The use of robotics in medicine raises ethical questions regarding patient consent, data privacy, and the potential for reduced human interaction in patient care. It is essential for healthcare providers to navigate these ethical considerations thoughtfully.
4. The Future of Robotics in Medicine
The future of robotics in medicine looks promising, with ongoing research and development aimed at enhancing existing technologies and creating new applications. Potential advancements include:
4.1 AI Integration
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with robotics could lead to even more sophisticated systems capable of making real-time decisions during surgeries or diagnostics. AI could analyze vast amounts of data to assist in post-operative care and rehabilitation.
4.2 Telemedicine Robotics
Telemedicine is gaining popularity, and robotics could further facilitate remote surgeries and consultations. Robotic systems that can be controlled remotely will allow surgeons to perform procedures from different locations, expanding access to specialized care.
4.3 Personalized Medicine
As personalized medicine continues to evolve, robotics may play a significant role in tailoring treatments to individual patients. Robotic systems could be designed to adapt to specific patient needs, enhancing treatment efficacy.
Conclusion
The impact of robotics in medicine is profound and multifaceted. From enhancing surgical precision to improving patient care and operational efficiency, robotics represents a significant advancement in healthcare. As technology continues to evolve, the integration of robotics will likely play an even more critical role in shaping the future of medicine. Embracing these innovations will not only improve patient outcomes but also redefine the landscape of healthcare delivery for generations to come.
Rate the Post
User Reviews
Popular Posts